No products in the cart.
Hinduism, Vedic Philosophy
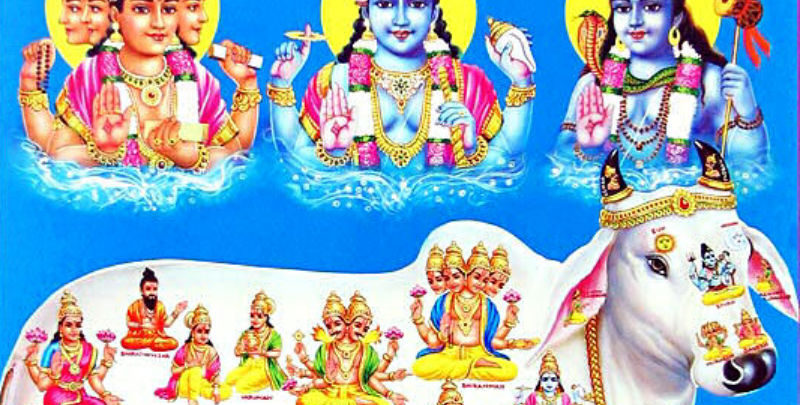
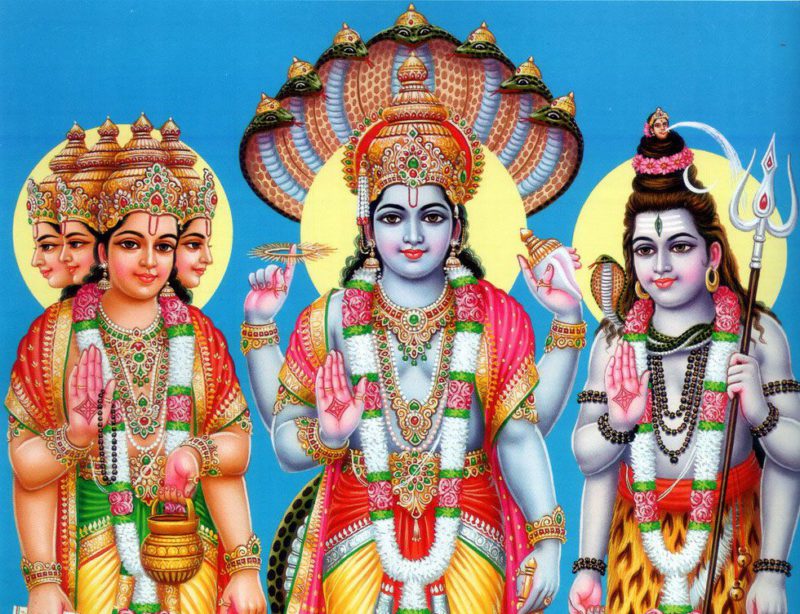
Kamadhenu – Significance of Gomatha in Hinduism
‘Kamadhenu’ the Celestial Cow assures fulfillment of well deserved needs in both the contexts of ‘iham and param’ or during the ongoing and subsequent lives’. The popular Picture Post Cards depict Kamadhenu with its forehead ‘s upper part as of Parama Shiva with the symbolic AUM as the saffron spot while its nether part just […]